Chatbots have significantly evolved over the years, emerging from simple tools for answering basic questions to sophisticated AI-driven systems capable of engaging in meaningful and dynamic conversations.
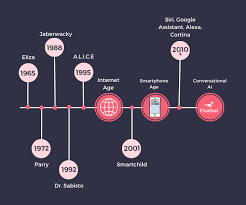
From their early beginnings in the 1960s to the powerful virtual assistants we rely on today, chatbots have transformed industries and the way humans interact with machines.
In this narrative, we will explore the history of chatbots, their technological development, the milestones in their evolution, and how they are shaping the present and future of communication.
The Evolution of Chatbots
1. Early Beginnings: The 1960s and ELIZA
The concept of chatbots dates back to the 1960s when Joseph Weizenbaum, a professor at MIT, developed one of the first-ever chatbots, named ELIZA. ELIZA was designed to simulate conversation by using pattern-matching techniques and simple scripted responses. Weizenbaum’s goal was to create a program that could mimic the behavior of a psychotherapist, helping users feel as though they were having a conversation with a human.
ELIZA used a technique called “pattern matching”, where it identified key phrases in the user’s input and responded based on predefined scripts. For example, if a user mentioned feeling sad, ELIZA might respond with a question like, “Why do you feel that way?” While rudimentary by today’s standards, ELIZA’s simple interactions marked a significant first step in conversational agents.
2. The Rise of Expert Systems: 1970s-1980s
During the 1970s and 1980s, the concept of expert systems began to emerge. These systems were designed to simulate the decision-making abilities of a human expert in a specific field. Expert systems were primarily rule-based and used logic and databases of knowledge to answer questions in specialized domains such as medicine, law, and customer service.
While these systems were not strictly chatbots in the modern sense, they were foundational in showing the potential of AI to provide intelligent, context-driven responses. They were typically used for highly structured tasks and lacked the conversational flexibility of today’s chatbots.
3. The Age of Personal Assistants: 1990s-2000s
As the 1990s and early 2000s approached, the world saw the development of personal assistant programs and chatbots that could provide more conversational, task-oriented interactions. Some notable examples from this era include ALICE (Artificial Linguistic Internet Computer Entity) and Jabberwacky.
- ALICE (1995): Developed by Dr. Richard Wallace, ALICE was a chatbot that used an extensive set of rules and pattern-matching algorithms to engage in text-based conversations. Unlike ELIZA, ALICE had a more complex set of responses, and its interactions were less predictable. The chatbot won the Loebner Prize (an annual Turing Test competition) three times, which helped cement its place in chatbot history.
- Jabberwacky: Created by Rollo Carpenter in the late 1990s, Jabberwacky was a chatbot that focused on engaging in casual conversations and learning from interactions with users. Its goal was to simulate a “human-like” conversation, and it was one of the first to use machine learning techniques to improve its responses over time.
Although these early personal assistants and chatbots were a step forward, they were still limited in terms of processing power, language understanding, and the complexity of the conversations they could handle.
4. The Birth of Smart Virtual Assistants: 2010s
The real breakthrough in chatbot technology came with the rise of virtual assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, Amazon Alexa, and Microsoft’s Cortana. These intelligent systems relied on cloud-based AI, machine learning, and natural language processing to provide more sophisticated conversational abilities.
- Google Assistant (2016): Google Assistant built on the company’s expertise in search and AI to create a more powerful virtual assistant. It could engage in two-way conversations, set reminders, provide weather updates, and much more. Unlike Siri, Google Assistant excelled in its ability to answer complex questions by leveraging Google’s search algorithms.
- Amazon Alexa (2014): Amazon’s Alexa revolutionized home automation by allowing users to control smart devices, play music, and perform other tasks through voice commands. It was an early leader in integrating chatbots with IoT (Internet of Things) devices, paving the way for the smart home ecosystem.
5. AI and NLP Revolution: Late 2010s-Present
In recent years, the development of advanced deep learning models has dramatically enhanced the capabilities of chatbots. With the advent of transformer-based models like GPT-3 (and its successor, GPT-4), chatbots have become far more capable of understanding context, handling complex queries, and producing human-like text.
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers): Developed by Google in 2018, BERT improved the accuracy of NLP models by understanding words in context rather than as isolated terms. BERT and similar transformer models significantly improved search engines, chatbots, and virtual assistants by providing more accurate, nuanced interpretations of natural language.
These models paved the way for chatbots that not only understand commands but also engage in fluid, intelligent conversations that seem far more human-like than ever before.
6. Modern-Day Chatbots: Integration and Multitasking
- Multitasking Chatbots: Modern chatbots are now capable of performing multiple tasks at once. For example, a user could ask a virtual assistant to play music while also setting an alarm and checking the weather. The integration of AI into these systems means that chatbots can handle more complex scenarios involving multiple steps.
- Multilingual Capabilities: Thanks to advancements in NLP, many modern chatbots can understand and respond in multiple languages, opening up new opportunities for global communication and customer support.
- Sentiment Analysis: Modern chatbots have the ability to analyze the sentiment behind a user’s input, allowing them to adjust their responses accordingly.
READ ALSO: How to Center Your Instagram Bio (Easy Methods)
7. Future of Chatbots: Trends and Prospects
The future of chatbots is incredibly exciting, with advances in emotion AI, multimodal interaction, and personalized experiences on the horizon. Some key trends include:
- Emotion AI: Future chatbots may be able to recognize and respond to emotions in real time, offering more empathetic and human-like interactions.
- Multimodal Communication: Chatbots will increasingly incorporate voice, text, and visual inputs, creating a richer and more immersive experience for users.
- Hyper-Personalization: With AI’s ability to gather and process vast amounts of data, chatbots will offer highly personalized services tailored to individual user preferences and needs.
FAQs
Can chatbots understand emotions?
Some advanced chatbots are being equipped with emotion AI to recognize the sentiment behind a user’s text or speech. This allows them to adjust their tone or responses accordingly, though true emotional understanding is still a developing area of research.
How do chatbots improve over time?
Many modern chatbots use machine learning and deep learning algorithms, which allow them to learn from interactions and improve their responses over time. Additionally, chatbots built on advanced models like GPT-4 can generate more accurate and contextually relevant responses based on prior conversations.
What are the ethical concerns surrounding chatbots?
Ethical concerns about chatbots include issues related to privacy, data security, and bias in AI models. There is also concern about the potential for chatbots to deceive users into thinking they are conversing with a human, raising questions about transparency and trust.