In the fast-paced world of technology, ensuring that your computer performs at its best is crucial. Whether you’re working on important projects, gaming, or simply browsing the internet, a sluggish computer can be frustrating and counterproductive.
Over time, even the most powerful machines can start to slow down due to clutter, outdated software, or other issues. Fortunately, optimizing your computer is often simpler than it may seem.
In this guide, we’ll explore several techniques to help you maximize your computer’s performance and make it run faster and more efficiently.
1. Clean Up Your Hard Drive
One of the main reasons for a sluggish computer is insufficient storage space or fragmented data. Over time, files accumulate and unnecessary programs, cache files, and old system restore points fill up your hard drive. Cleaning up your hard drive can significantly improve your computer’s speed.
How to Clean Up Your Hard Drive:
- Uninstall Unnecessary Programs: Go through your installed programs and remove any software that you no longer need. You can do this by navigating to the “Control Panel” on Windows or “Applications” on macOS.
- Windows: Open the “Control Panel” > “Programs” > “Programs and Features,” and uninstall unnecessary applications.
- Mac: Go to “Applications” and drag unnecessary apps to the trash.
- Delete Temporary Files and Cache: Temporary files, browser cache, and system logs can consume valuable disk space. Use built-in tools like Disk Cleanup (Windows) or third-party applications like CCleaner (for both Windows and Mac) to clear unnecessary files.
- Use Disk Cleanup (Windows): Windows comes with a built-in Disk Cleanup tool that removes temporary files, system files, and empty directories.
- To use it: Open the “Start Menu,” type “Disk Cleanup,” select your hard drive, and click “OK.” The tool will analyze your drive and present a list of files to delete.
- Optimize File Storage with Cloud or External Drives: If you’re running low on disk space, consider moving non-essential files (e.g., documents, photos, videos) to cloud storage services like Google Drive or Dropbox. Alternatively, use external hard drives to offload large files.
2. Upgrade Your Hardware
Sometimes, optimizing performance requires upgrading your computer’s hardware. While software optimizations can go a long way, physical upgrades can provide a significant boost in speed and efficiency.
Key Hardware Upgrades to Consider:
- Install More RAM (Random Access Memory): RAM plays a crucial role in how quickly your computer processes tasks. If you find that your system slows down when running multiple applications or tabs, adding more RAM can help. Depending on your computer’s specifications, upgrading RAM can make a noticeable difference, especially for tasks like video editing, gaming, and multitasking.
- Upgrade to an SSD (Solid-State Drive): If you’re still using an HDD (Hard Disk Drive), upgrading to an SSD is one of the best performance boosts you can make. SSDs are significantly faster than HDDs in terms of read/write speeds, which will make your computer boot faster and programs load almost instantaneously.
- How to Replace Your HDD with an SSD: Check your computer’s compatibility for SSD installation (especially laptops), then use tools like Macrium Reflect or Samsung Data Migration software to clone your existing hard drive to your new SSD before making the switch.
- Upgrade Your Graphics Card (for Gaming or Design Tasks): If you’re into gaming or work with design-heavy applications (like Adobe Creative Suite or 3D modeling), upgrading your graphics card (GPU) can drastically improve performance. A more powerful GPU allows for smoother visuals, faster rendering times, and overall better system performance.
3. Update Your Software and Drivers
Outdated software or drivers can cause system instability, crashes, and poor performance. Keeping your operating system, applications, and drivers up-to-date ensures your computer is working with the latest performance improvements and security patches.
How to Update Software and Drivers:
- Windows Update (for Windows users): Windows automatically checks for updates, but you can manually initiate it by going to “Settings” > “Update & Security” > “Windows Update.” Make sure both system and security updates are installed regularly.
- macOS Software Update (for Mac users): For Mac users, updates are handled through the “App Store” or the “System Preferences” menu. Always keep your macOS up-to-date for optimal performance and security.
- Update Drivers: Drivers are small programs that help your hardware communicate with your operating system. Outdated drivers can cause performance issues, especially for your graphics card, network adapters, and peripherals. To check for updates:
- Windows: Open “Device Manager” > Right-click your hardware (like “Display Adapters” for graphics) > “Update Driver.”
- Mac: macOS typically handles driver updates automatically through software updates. However, for third-party peripherals, visit the manufacturer’s website for specific driver updates.
- Update Software Programs: Check for updates on software you frequently use. Many applications, especially web browsers, antivirus programs, and productivity software, release updates that improve performance and fix bugs.
READ ALSO: 10 Reasons Why Oculus Quest 2 is the Best VR Experience for Gamers
4. Disable Unnecessary Startup Programs
When you boot up your computer, several programs automatically launch, consuming resources and slowing down the startup process. Disabling unnecessary startup programs will improve boot times and overall performance.
How to Disable Startup Programs:
- Windows: Open “Task Manager” (Ctrl + Shift + Esc) and go to the “Startup” tab. Here, you can disable unnecessary applications that launch automatically when you start your computer. Be careful not to disable important programs like your antivirus.
- Mac: Go to “System Preferences” > “Users & Groups” > “Login Items.” Here, you can remove unnecessary startup items to speed up your Mac’s boot time.
5. Adjust Visual Effects and Power Settings
Modern operating systems come with attractive visual effects, such as animations and transitions, which can consume system resources. Adjusting these effects can free up CPU power and RAM, improving performance.
How to Adjust Visual Effects:
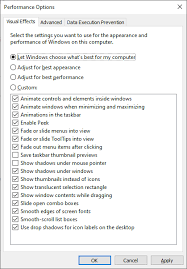
- Windows: Open “System Properties” > “Advanced System Settings” > “Settings” (under the Performance section). Here, you can choose to adjust for best performance by disabling all unnecessary visual effects, or manually disable specific effects like animations and shadows.
- Mac: While macOS doesn’t have the same level of customizable visual effects as Windows, you can still disable some effects for improved performance. Go to “System Preferences” > “Accessibility” > “Display” and check “Reduce motion” and “Reduce transparency” to minimize system strain.
Adjust Power Settings:
- Windows: Go to “Control Panel” > “Power Options” and choose the “High Performance” plan, which prioritizes performance over energy savings.
- Mac: In “System Preferences” > “Energy Saver,” select the option that prioritizes performance. For laptops, ensure that the computer is plugged into power when performing demanding tasks.
6. Run Antivirus and Malware Scans
Viruses, malware, and other malicious software can significantly slow down your computer, making it feel sluggish and unresponsive. Running regular antivirus scans can help keep your system clean and performing well.
How to Run Antivirus and Malware Scans:
- Windows: Use Windows Defender (built-in) or install third-party antivirus software like Avast, Bitdefender, or Malwarebytes. Run full system scans to detect and remove threats.
- Mac: macOS is less prone to malware than Windows, but it’s still a good idea to run periodic malware scans. Use tools like Malwarebytes for Mac to check for any malicious software.
7. Perform System Optimization Tasks Regularly
Running periodic system optimizations will ensure that your computer stays in top shape over time. This includes defragmenting your hard drive (if you’re using an HDD) and performing other routine maintenance tasks.
Routine Maintenance Tasks:
- Defragment Your Hard Drive (Windows users): If you’re using a traditional hard drive (HDD), periodic defragmentation helps organize data and improve read/write speeds. To defrag: Open “Start Menu” > “Defragment and Optimize Drives” > “Optimize.”
- Check for Disk Errors: Running a disk check on your hard drive can detect and fix potential errors. To do this, open “This PC,” right-click your hard drive, select “Properties” > “Tools” > “Check” under Error Checking.
FAQs
How often should I clean up my computer?
It’s a good practice to clean up your computer every couple of months. However, if you notice performance issues like slow boot times or lagging applications, it’s a good idea to perform cleanup and optimization tasks more frequently.
Can upgrading my RAM speed up my computer?
Yes, upgrading your RAM can help improve performance, especially if you’re running multiple applications or heavy programs like video editing software or games. More RAM means more memory for programs to run smoothly.
Should I get an SSD if I’m using a laptop?
Yes, upgrading to an SSD in a laptop can provide a huge performance boost, especially in terms of boot times, file transfer speeds, and overall system responsiveness. It’s one of the most effective upgrades for any computer.
How do I check if my computer has a virus?
If your computer is slow or acting unusually, it could be infected with a virus or malware. Run a full system scan with an updated antivirus program to check for infections.
Is it worth investing in a graphics card for better performance?
If you use your computer for gaming, video editing, 3D rendering, or other graphically intensive tasks, upgrading your graphics card can significantly improve performance. For everyday tasks, however, it may not be necessary.